Setting up a company in China – what roles are in the corporate management?
Action Plan:
Figuring out who to appoint for the following roles:
- Shareholder
- Authorized signatory of the shareholder
- Board of Directors/ Executive Director
- Legal Representative
- General Manager
- Supervisor
Who should be the shareholder?
Individual versus a Company
Are you going to more or less liability as an individual or more or less liability as a Company?
It is better to have company as the shareholder for lesser liability and would be good considering the taxation.
Do I need to consider an offshore holding company?
Reduce tax rate based on the Double Taxation Agreements,
Make it easier and faster the change in capital or shareholder ship,
But Indirect transfer of assets: An investor that has structed an equity interest in a Mainland Chinese company through an offshore holding company could it, if the investor sells interests in the offshore company, be subject to an additional tax burden within China.
It is necessary that the offshore holding has substance in its jurisdiction, in order to avoid any risk with the Chinese Law.
Case Study 1 : High Turnover of corporate management
- SME in Canada incorporating their company in China
- Within the first 2 years of operation, they spent over RMB 80,000 in lawyers’ fees to change the international corporate structure
- Continuous resignation in C-level positions in the headquarter which caused disruptions for the China company.
Case Study 2: Termination of Individuals in the Corporate Structure
- SME in Italy established in China for a number of years
- The legal representative was an Italian, having relocated to China to manage the subsidiary
- Italian HQ decided to terminate his employment – ‘’forgetting’’ he was appointed as legal representative
- Documents needed to be signed by a legal representative – nobody on hand – as the legal representative
- Tried to indicate that the legal representative had ‘’died’’
Case Study 3: No replacement for individuals within the corporate structure
- SME in the US incorporated their China subsidiary
- Legal representative was the Head of Asia Pacific operations (logical choice) – everything was perfect until…
- He resigned
- For one year and half he was still the legal representative of the China subsidiary because the US HQ could not decide or find a replacement
- The individual threatened suing the company as for this one year and half he was the ‘’legal-face’’ to the entity in China. If anything, ‘’bad’’ were to occur, he would be liable – worst case prevented from entering China hence affecting his new role and position.
The Corporate Structure in China
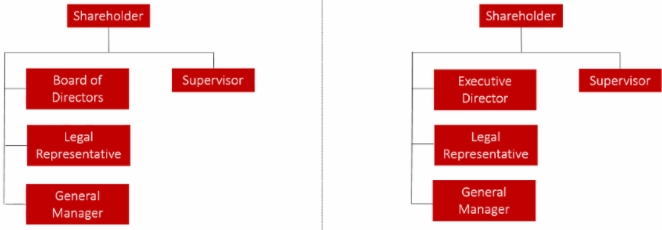
Criteria of these individuals:
- DO NOT need to reside in China
- Should be responsible for the China business – do not pick at random
- Board of Directors – By default Chairman is Legal Representative
- Member of the Board can be the legal Representative who can be the General Manager
- Executive Director can be the Legal Representative who can be the General Manager
- Supervisor CANNOT be a member of the Board, CANNOT be the Legal Representative and CANNOT be the General Manager
Responsibilities of the Board or Executive Director
- Convening the Shareholders’ meeting and report to the Shareholders;
- Executing the Shareholders’ resolutions;
- Working out the corporate strategy and the company’s investment plans;
- Working out the company’s annual financial budget plans and final accounting plans;
- Working out the company’s profit distribution plans and loss recovery plans;
- Working out the company’s plans on the increase or decrease of the registered capital and/or the total investment amount, as well as on the issuance of corporate bonds;
- Working out the company’s M&A plans concerning possible divisions, dissolutions or liquidations of the company as well as the change of the company’s legal form;
- Appointing and dismissing the General Manager and determining his renumeration as well as upon the determining their renumerations;
- Working out the basic rules and policies of the company;
- Other responsibilities as stipulated by the Shareholder (s) in the Articles of Association
Liabilities of the Legal Representative
For instance, in accordance with the Article 49 of the General Principles of the Civil Law of the People’s Republic of China, the Limited Liability Company should stay liable, and its Legal Representative may additionally be sentenced with the administrative sanctions or penalties if any of the following circumstances are applicable. If the offence constitutes a crime, criminal responsibility shall be investigated in accordance to the law:
- Conducting illegal operations beyond the range approved and registered by the registration authority;
- Concealing facts from the registration and tax authorities and practicing fraud:
- Secretly withdrawing funds or hiding property to evade the repayment of debts;
- Disposing of property without authorization after the enterprise has been dissolved, disbanded or declared bankrupt;
- Failing to apply for registration or not making a public announcement promptly in case the enterprise undergoes substantial changes or closes completely, which can cause heavy losses to the people invested in the company;
- Engaging in other activities prohibited by law, damaging the interest of the state or the public interest.
Responsibilities of the General Manager
- Supervising the business operations of the company and implement the resolutions of the Board or the Executive Director;
- Executing the company’s annual operational plans and investment plans;
- Formulating plans on the establishment of the company’s internal management departments;
- Drafting the company’s basic management system;
- Drafting the company’s specific policies;
- Proposing the appointment and dismissal of the company’s Deputy Manager(s) and the Financial Manager(s);
- Deciding on the appointment or dismissal of Executive Personnel other than those whose appointment of dismissal Is to be decided by the Board or Executive Director; and
- Any other function or power authorized by the Board or Executive Director.
Responsibilities of the Supervisor
- Inspecting the financial affairs of the company;
- Supervising the performance and duties of the Directors and the Senior Managers and proposing the removal of any Director or Senior Manager who violates any law, administrative regulation, the Articles of Association or any resolution of the Shareholder’s meetings
- Requiring any Director or Senior Managers to take corrective action if his/her actions damage the interests of the company;
- Proposing the convention of Interim Shareholders’ meeting and disclosure and disclosure any misbehavior at which the Board of Directors/Executive Director has not exercised its functions prescribed by law;
- Putting forward proposals at Shareholder’s meeting;
- Initiating lawsuits against a Director or Senior Management; and
- Any other function or power specified in the Articles of Association.
Power of Authority
Allocating the power
Delegating power always requires a degree of trust BUT there are a few simple measures every foreign investor should consider to mitigate the risks its Chinese subsidiary is exposed to.
Allocating power to the Legal Representative
- Do not involve the legal representative too much in the daily operations of the company.
- Foreign investors may consider appointing a legal representative that does not reside in China, whose signature is only required 2 or 3 times a year.
- Obtain signed copies of signature sheets that undated for security purposes – not just for the legal representative, but for all individuals within the corporate structure
Allocating power to the General Manager
- Don’t appoint the general manager, if you have only known the individual for less than a year.
- Don’t give the general manager unrestricted access to the company’s chops. Set rules for the use chops, such as requiring major decisions to also bear the chop or signature of the director, supervisor or legal representative.
- Investors can also hire a third party to act as custodian of the company chops and seals.
- Limit the powers of the general manager in the articles of the association. This could include capping the amount of money a general manager can deal with.
- Carefully plan who are the signatories on the bank account – is the general manager able to gain access?
Allocating power to use the company chops and seals
- A company is bound whenever a contract or other documents is affixed with the company seal or chop
- This is more straightforward in the sense that one can immediately tell whether a company has approved the content of a document or not.
- What makes it dangerous, however, is that whoever holds the chops can bind the company.
- On top of that, there is the risk of forged chops.
China have different kinds of chops for different purposes:
- Company chop
- Finance chop
- Contract chop
- Invoice chop
- Customs chop
- Legal Representative chop
Note: The company, finance and customs chop ate mandatory, while the contract chop can be replaced by the company chop and the invoice chop be the finance chop. The company, finance and legal representative chop (if present) need to be recorded with the Public Security Bureau, the Administration of Industry and Commerce (AIC), and with the local bank.
Action plan: Questions to ask your management about the China operations
- Who or what is making the Investment into China? A company or an individual?
- Who is the China company decision maker?
- Who will be the Chief Financial Officer/ Finance Manager?
- Who will be the bank signatory OR who will be approving payments?
- Who will keep control of the company chops?
For any information on how to choose the right people for your corporate management in China, please contact our team by email at info@opkofinance.com or by phone at +852 2654 8800/+86 187 177 31958.