Personal income tax (PIT) declaration, settlement, and payment are very important tasks for not only the employer but also the employee, especially when a foreign employee is recruited and working in Vietnam.
Some key notes for your Annual PIT – personal income tax settlement as follows:
PERSONAL INCOME TAX
There are 9 typical taxable incomes:
- Incomes from business are incomes which earned from the production and sale, in particular
- Incomes from production and sale of goods and services that belong to all industries such as production, goods sale, construction, restaurants, service provision including the lease of houses, right to use the land, water surface, and other property.
- Incomes from freelance works of individuals in the fields that are licensed or certified as prescribed by law.
- Incomes from wages and remunerations which paid to employees from employers, including
- Wages, remunerations, and the other amounts paid as wages or remunerations in cash or not in cash.
- Allowances and benefits
- Occupational benefits
- Remunerations in the forms of agent commission, brokerage commission, payments for participation in science and technology researches, payments for participation in projects and schemes, royalties according to regulations of law on royalties, payments of teaching, payments for participation in artistic performance, sports, payments for advertising, payments for other services, and other remunerations.
- Payments for participation in business associations, Board of Directors, Control Boards, project management boards, management councils, professional associations, and other organizations.
- Other benefits in cash or not in cash apart from wages paid to the taxpayer by the employer in any shape or form: Payments for housing, electricity, water supply, and ancillary services (if any); The life insurance premiums, other optional insurance premiums, contributions to the voluntary pension fund paid or made by the employer on the employee’s behalf; Membership fees and other expenditure on services serving individuals such as healthcare, entertainments, sports, recreation; Flat expenditures on stationery, business trips, phone calls, costumes, etc. that are in excess of limits prescribed by the State; Rewards in cash or not in cash in any shape or form, including rewards in the form of securities.
- Incomes from capital investment
- Interest on the loans given to other organizations, enterprises, business households, business individuals, and groups of business individuals according to loan contracts or agreements.
- The dividends are earned from capital contribution to the purchase of shares.
- The incomes from capital investment in other forms, including capital contribution in kind, by reputation, rights to use the land, patents.
- Incomes from dividends, pain in bonds, incomes from reinvested profit.
- Incomes from capital transfer
- Profits from capital contributions to limited liability companies (including single-member limited liability companies), partnerships, cooperatives, business cooperation contracts, people’s credit funds, economic organizations, and other organizations.
- Incomes from securities transfer, including incomes from transferring shares, call options on shares, bonds, treasury bills, fund certificates, and other securities according to the Law on Securities; incomes from transferring shares of the persons in the joint-stock company according to the Law on Enterprises.
- Incomes from real estate transfer
- Incomes from transferring rights to use land.
- Incomes from transferring rights to use land and property on the land.
- Incomes from transferring ownership of houses, including future houses.
- Incomes from transferring rights to use the land, rights to rent water surface.
- Incomes from delegating the management of the real estate, if the person delegated to manage real estate has the right to transfer real estate or similar rights to the real estate owner.
- Incomes from winning prizes
- Winning lottery prizes
- Winning prizes from promotion programs when buying products or services according to the Law of Commerce.
- Winning prizes from the type of betting permitted by law.
- Winning prizes in the casino permitted by law.
- Incomes from copyright
- Incomes from copyright are incomes from the transfer of ownership, rights to use the subjects of intellectual property rights according to the Law on Intellectual property, incomes from technology transfers according to the Law on Technology transfers. In particulars:
- The subjects of intellectual property rights.
- Subjects of technology transfers
- Incomes from franchising
- Incomes from copyright are incomes from the transfer of ownership, rights to use the subjects of intellectual property rights according to the Law on Intellectual property, incomes from technology transfers according to the Law on Technology transfers. In particulars:
- Incomes from inheritance
- Inherited securities: shares, call options on shares, bonds, treasury bills, fund certificated, and other securities according to the Law on Securities; share of the person in the joint-stock company according to the Law on Enterprises.
- Inherited capital in economic organizations and businesses: capital contribution to limited liability companies, cooperatives, partnerships, business cooperation contracts; capital in private enterprises and businesses of the person; capital in associations and funds established within the law, or the entire business if the private enterprise or business is under the ownership of the person.
- Inherited real estate: rights to use the land, rights to use lang and property thereon; ownership of houses, including future houses, infrastructure and constructions on land, including the off-the-plan constructions; rights to rent land or water surface; other incomes from inheritance being real estate in any shape or form.
- The ownership and use rights of other inherited assets (cars, motorbikes, ships, barges, speedboats, towboats, yachts, airplanes, hunting guns, sporting guns) must be registered with state agencies.
- Incomes from receipt of gifts
- Incomes from receipt of gifts are incomes the person received from organizations and individuals at home and overseas, in particular:
- Gifts being securities: shares, call options on shares, bonds, treasury bills, fund certificates, and other securities according to the Law on Securities; shares of the person in the joint-stock company according to the Law on Enterprises.
- Gifts being capital in economic organizations and businesses: capital contribution to limited liability companies, cooperatives, partnerships, business cooperation contracts; capital in private enterprises and businesses of the person; capital in associations and funds established within the law, or the entire business if the private enterprises or business is under the ownership of the person.
- Gifts being real estate: rights to use the land, rights to use land and property thereon; ownership of houses, including future houses, infrastructure, and constructions on land, including off-the-plan constructions; rights to rent land or water surface; other incomes from inheritance being real estate in any shape or form.
- The ownership and use rights of gifts being other assets (cars, motorbikes, ships, barges, speedboats, towboats, yachts, airplanes, hunting guns, sporting guns) must be registered with state agencies.
PERSONAL INCOME TAX STATEMENT AND TAX SETTLEMENT
The payer of taxable incomes and the person that earns taxable incomes shall declare tax and settle tax in accordance with the local procedures.
Rules for declaring tax in some cases:
- Foreign employees who should directly declare tax at tax authorities
- The residents that earn incomes from wages and directly declare tax at tax authorities include: The residents that warn incomes from wages paid by international organizations, embassies, and consulates in Vietnam without withholding tax shall directly declare tax quarterly at tax authority; The residents that earn incomes from wages paid by overseas organizations and individuals shall directly declare tax quarterly at the tax authorities.
- If one staff member does not join a company for a full 12 months or has personal income tax from wages/ salary from other companies. In this case, these staff cannot request income payers to settle tax on their behalf but directly declare tax at tax authorities.
- To make a declaration, he or she must prepare a letter of income confirmation from the previous income payer + certificate of tax withheld at source on the incomes (withheld receipt). Based on income from the current company and other incomes with the withheld receipts, they should prepare the annual settlement sheet and declare it directly to the tax department. This task is not an employer’s obligation but a personal matter of every staff member (it means, the annual final settlement sheets of the company will not be including his or her sheets).
- Foreign employees who will pay tax on the progressive method of applying the fixed rate
- To verify a proper method of personal income tax (PIT) declaration for expats, the tax officer will base on the passport, labour contract appointment letter/ tax withheld receipts, rental contract.
- If you are a resident or non-resident, you should declare a settlement of PIT for the incomes inside Vietnam of either global income. Taxable amounts/tax rates of residents and non-resident are completely different. Failure to apply properly declaration of PIT will lead to serious fines from the tax department in the coming years.
- A good consultant will support you to manage standard employee profiles/ legal requirement records as well as compliance reports/ declarations to guarantee your files are right the first time, clean and clear today, and for the next 3 or 5 years.
- Typical cases that tax statements made by payers of taxable income
- The income payers that withhold personal income tax shall declare tax monthly or quarterly. The income payer might not declare tax if no personal income tax is withheld in the month or in the quarter.
- The monthly or quarterly tax statement shall be made from the first month in which tax is withheld, and is applicable to the whole tax year.
- Typical cases that tax statements made by residents that earn incomes from wages and business
- The residents, groups of residents that earn incomes from business and directly declare tax at tax authorities include:
- The businesspersons, groups of business persons that pay tax according to tax statements are the business persons, groups of business persons that comply with regulations of law on accounting and invoicing, and the business persons, groups of business persons that fail to separate expenses from revenue and declare tax quarterly;
- The business person, group of business persons that pay flat tax is the business person, group of business persons that do not comply with the regulations of law on accounting and invoicing and fail to determine revenue, expense, and taxable income shall declare tax annually
- The nomadic business persons shall declare personal income tax every time it is incurred; The business persons that use invoices sold separately by tax authorities shall declare personal income tax every time revenue is earned; The non-business persons that sell goods and services and need to issue invoices to their customers shall declare tax when it is incurred; The person or group of persons that earn income from leasing outhouses, rights to use land, water surface, and other property shall declare tax quarterly or every time it is incurred.
- The person that earns income from wages, a business shall settle tax when tax is incurred or paid or offset against the next period, except for the cases: The person whose tax payable is tax smaller than provisional tax paid does not apply for a tax refund or offset it against tax the next period
- The person or business households has only one source of income from business and has paid a flat tax
- The person or household only earns income from leasing outhouses, rights to use land, and have a paid tax according to a declaration in the locality where such houses or land are situated
- The wage-earner signed a labour contract for 03 months or more with a unit and earns average monthly income of no more than 10 million VND from other places in the year, 10% tax on which has been withheld at source by the income payer. This income shall not be declared without the request of the person;
- The wage-earner signed a labour contract for 03 months or more with a unit, earns an average monthly income of no more than 20 million VND from leasing houses, rights to use land in the year, and has paid tax in the locality where such houses or land are situated. This income shall not be declared without the request of the person.
- The wage-earner shall request another organization or person to settle tax on their behalf in the following cases:
- The person that only earns incomes from wages signed a labour contract for 03 months or more in a unit and is actually working at that unit when delegating the making of tax statement, even he has not worked for 12 months in the year
- The wage-earner signs a labour contract for 03 months or more and earns other incomes; The income payer shall only settle tax on the income that the pay on the person’s behalf.
- The residents, groups of residents that earn incomes from business and directly declare tax at tax authorities include:
- Rules for settling tax
- The resident that earns an income overseas and has to pay personal income tax on that income overseas shall have the tax paid overseas deducted. The amount of tax deducted shall not exceed the tax payable on the income earned overseas according to Vietnam’s tax table. The ratio is based on the ratio of income earned overseas to the total taxable income.
- The persons earns incomes from wages and has been present in Vietnam in the first calendar year for fewer than 183 days, but has been present in Vietnam for 183 days or more within12 consecutive months from the date of arrival, the first tax period is 12 consecutive months from the date of arrival, the second year, the tax period is the calendar year.
- In the first tax year: make and submit the tax settlement form by the 90th day from the end of the 12 consecutive months.
- From the first tax year: make and submit the tax settlement form by the 90th day from the end of the calendar year. The remaining tax payable in the second tax year is calculated as follows.
- The resident who is a foreigner terminates the labor contract in Vietnam and settles tax at the tax authority before departure.
- The person that leases outhouses, rights to use the land, water surface, and other property shall settle personal income tax.
- The person that declares tax monthly or when it is incurred under a contract that is due within 01 year shall settle tax, in the same way, the persons that pay tax according to declarations do.
- The persons that earn incomes form the insurance agents, lottery agents, or network marketing shall directly settle tax at the tax authorities if required.
- The persons that earn incomes from wages, business, and are eligible for tax reduction due to natural disasters, fire, accidents, fatal diseases shall directly settle tax at tax authorities.
- The non-resident business persons, groups of business persons that have fixed business premises in Vietnam shall settle tax in the same way residents do.
TAX RATES
Who is the resident:
- The person has been present in Vietnam for 183 days or longer in the calendar year, or for 12 consecutive months from the day on which that person arrives in Vietnam (the date of arrival and date of departure are considered 01 days). The date of arrival and date of departure depends on the certification of the immigration agency on the passport (or laissez-passers) when that person enters and leaves Vietnam. If the person enters and leaves Vietnam within one day, it is considered a day of residence.
- The person has a regular residence in Vietnam:
- For Vietnamese citizens: the regular residents is the place where that person regularly, stable, and indefinitely lives and has been registered as a permanent resident as prescribed by regulations of law on a resident.
- For foreigners: the regular resident is the permanent written in the permanent resident card, or the temporary resident when applying for the temporary resident card issued by competent authorities.
NON-RESIDENTS ARE THE PERSONS THAT FAIL TO MEET THE ABOVE CONDITIONS
Tax rate and calculating tax incurred by non-residents
- The rate of personal income tax on incomes from wages earned by a non-resident equals the taxable income from wages multiplied by (x) 20% tax. The taxable income from wages earned by a non-resident is similar to that of a resident guided above.
- The taxable income from wages earned in by a non-resident that works both in Vietnam and overseas without being able to separate the income earned in Vietnam shall be calculated as follows:
A. WHEN THE FOREIGNER IS NOT PRESENT IN VIETNAM
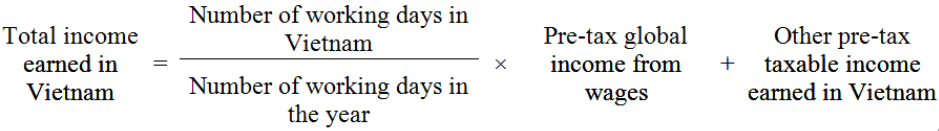
The number of working days in the year is calculated in accordance with the Labor Code of Vietnam.
B. WHEN THE FOREIGNER IS PRESENT IN VIETNAM:
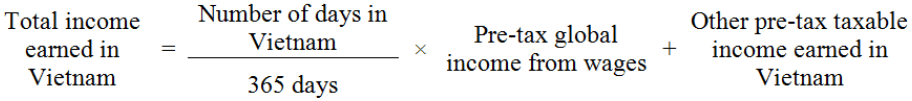
Other pre-tax taxable incomes earned in Vietnam mentioned above are other benefits in cash or not in cash apart from wages that are provided for the employee or paid on the employee’s behalf by the employer.
Tax rate and calculating tax incurred by residents on taxable incomes from business, wages
The basis for calculating tax on income from business wages is the assessable income and tax rate. Assessable income equals taxable income minus (-) the following deductions:
- Personal deductions.
- Insurance premiums and payment to the voluntary pension fund.
- Charitable, humanitarian, and study encouragement contributions.
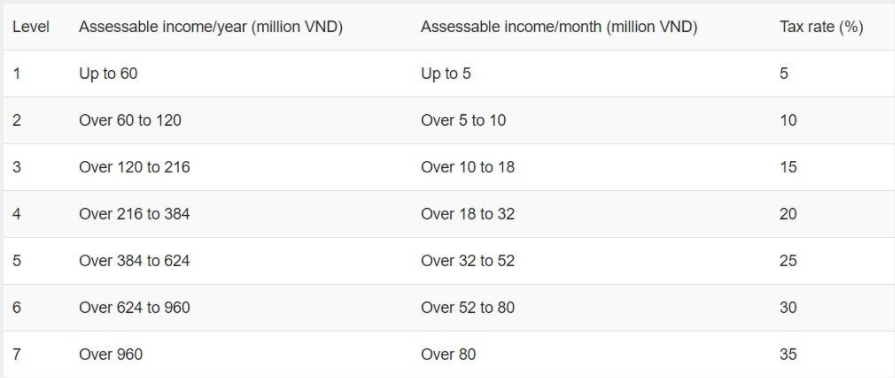
Tax rate
The rate of personal income tax on incomes from business, wages shall apply the progressive tax table, in particular:
For any information on Personal Income Tax in Vietnam, please contact our team by email at info@opkofinance.com or by phone at +852 2654 8800.








